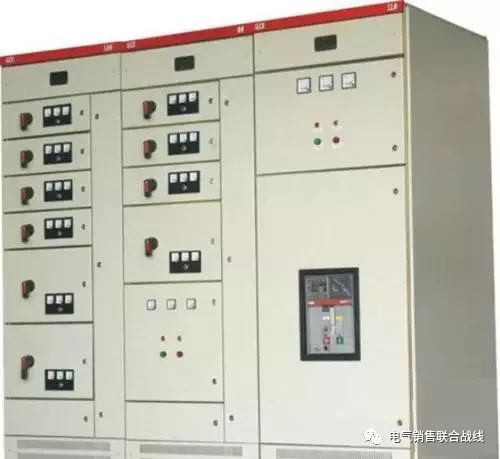
Switchgear refers to a complete set of power distribution devices assembled from primary equipment and secondary equipment according to a certain circuit scheme. It is used to control and protect the lines and equipment. It is divided into fixed type and handcart type. According to the voltage level of the incoming and outgoing lines, it can be divided into high-voltage switchgear (fixed type and handcart type) and low-voltage switchgear (fixed type and drawer type). The structure of the switchgear is generally similar, mainly divided into bus room, circuit breaker room, secondary control room (instrument room), and feeder room. There is generally a steel plate isolation between each room.
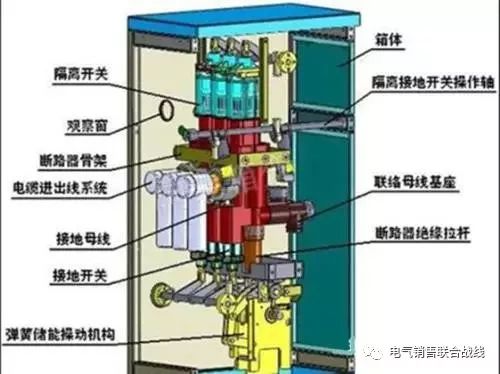
Internal components include: bus (bus), circuit breakers, conventional relays, integrated relay protection devices, metering instruments, isolation knives, indicator lights, grounding knives, etc.
From an application perspective:
(1) Incoming line cabinet: Also known as receiving cabinet, it is a device used to receive electrical energy from the power grid (from the incoming line to the bus), usually equipped with circuit breakers, CT, PT, isolation knives and other components.
(2) Outlet cabinets: also known as feeder cabinets or distribution cabinets, are equipment used to distribute electrical energy (from the bus to each outlet), and are generally equipped with circuit breakers, CT, PT, isolation knives, and other components.
(3) Busbar contact cabinet: Also called busbar break cabinet, it is a device used to connect two busbars (from busbar to busbar), and busbar contact is often used in single-busbar segmented and double-busbar systems to meet the requirements of users to choose different operating modes or to ensure selective cutting loads in case of failure.
(4) PT cabinet: voltage transformer cabinet, usually installed directly to the bus to detect bus voltage and achieve protection functions. Internal main installation of voltage transformer PT, isolation knife, fuse and arrester.

(5) Isolation cabinet: It is used to isolate the bus at both ends or to isolate the power receiving equipment and the power supply equipment. It can provide a visible endpoint to the operator to facilitate maintenance and overhaul operations. Since the isolation cabinet does not have the ability to break or connect the load current, it is not possible to push and pull the handcart of the isolation cabinet when the circuit breaker it matches is closed. In general applications, it is necessary to set the interlock of the auxiliary contact of the circuit breaker and the isolation handcart to prevent the operator from misoperation.